The BOOT Process ( Intermediate level ) Class 4.
Hi Friends,
Now, that we are ready : We have gone through Basics of Computer/hardware and software lets now begin the interesting journey.
The First STEP ( Once you press the power button ) We will see how the computer starts.
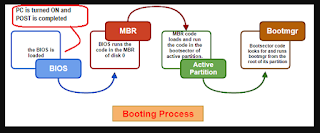
After the power button is pressed, it performs 'power on self test' POST.
POST checks a computer's internal hardware for compatibility and working status before starting the boot process. If the computer passes the POST, the computer may give a single beep and it starts to continue to boot.
However, if the computer fails the POST, the computer will generate a beep code that tells the user the source of the problem.
Any errors here can be identified by beep sounds ( as display drivers are not loaded yet and there is no display formed )
However, because of the wide variety of different computer manufacturers with this BIOS, the beep codes may vary.
For a DELL motherboard below are the codes.
1 beep - BIOS ROM corruption or failure
2 beeps - Memory (RAM) not detected
3 beeps - Motherboard failure
4 beeps - Memory (RAM) failure
5 beeps - CMOS Battery failure
6 beeps - Video card failure
7 beeps - Bad processor (CPU)
After POST, the BIOS ( Basic Input/Output system ) locates and reads the configuration settings that are stored in the CMOS memory. The boot device priority, is the order in which devices are checked to locate the operating system.
The boot device priority is set in the BIOS and can be arranged in any order. The BIOS boots the computer using the first drive that contains an operating system.
Hard drives, network drives, USB drives, and even removable magnetic media, such as CompactFlash or Secure Digital (SD) cards can be used in the boot order, depending on the capabilities of the motherboard.
Some BIOS also have a boot device priority menu that is accessed with a special key combination while the computer is starting but before the boot sequence begins. You can use this menu to select the device to boot.
At this point, the NT kernel takes over. The NT kernel is the heart of all Windows operating systems. The name of this file is NTOSKRNL.EXE. It starts the login file called WINLOGON.EXE and displays the Windows Welcome screen.
All the above mentioned files can be found in C:\Windows\System32.
Now, that we know how the Computer is started, Lets get more into it!
In the next blog - We will learn the differences between Operating systems.
Now, that we are ready : We have gone through Basics of Computer/hardware and software lets now begin the interesting journey.
The First STEP ( Once you press the power button ) We will see how the computer starts.
After the power button is pressed, it performs 'power on self test' POST.
POST checks a computer's internal hardware for compatibility and working status before starting the boot process. If the computer passes the POST, the computer may give a single beep and it starts to continue to boot.
However, if the computer fails the POST, the computer will generate a beep code that tells the user the source of the problem.
Any errors here can be identified by beep sounds ( as display drivers are not loaded yet and there is no display formed )
However, because of the wide variety of different computer manufacturers with this BIOS, the beep codes may vary.
For a DELL motherboard below are the codes.
1 beep - BIOS ROM corruption or failure
2 beeps - Memory (RAM) not detected
3 beeps - Motherboard failure
4 beeps - Memory (RAM) failure
5 beeps - CMOS Battery failure
6 beeps - Video card failure
7 beeps - Bad processor (CPU)
After POST, the BIOS ( Basic Input/Output system ) locates and reads the configuration settings that are stored in the CMOS memory. The boot device priority, is the order in which devices are checked to locate the operating system.
The boot device priority is set in the BIOS and can be arranged in any order. The BIOS boots the computer using the first drive that contains an operating system.
Hard drives, network drives, USB drives, and even removable magnetic media, such as CompactFlash or Secure Digital (SD) cards can be used in the boot order, depending on the capabilities of the motherboard.
Some BIOS also have a boot device priority menu that is accessed with a special key combination while the computer is starting but before the boot sequence begins. You can use this menu to select the device to boot.
At this point, the NT kernel takes over. The NT kernel is the heart of all Windows operating systems. The name of this file is NTOSKRNL.EXE. It starts the login file called WINLOGON.EXE and displays the Windows Welcome screen.
All the above mentioned files can be found in C:\Windows\System32.
Now, that we know how the Computer is started, Lets get more into it!
In the next blog - We will learn the differences between Operating systems.
Thank you for reading!
-Omair Sharif.
-Omair Sharif.
If you have any questions, please put in the comments box below and submit, I will response at the earliest. Thank you again.

Comments
Post a Comment